- Visual Studio for Mac distributes updates for the IDE and supported frameworks on a regular basis. These updates can be in the form of new features, improvements, and bug fixes. Visual Studio for Mac provides two channels to get these latest versions: Stable - Provides thoroughly tested updates. This channel is recommended for the best.
- Visual Studio Code for Mac is an integrated development environment (IDE) and the main focus with this version is it is clearly leaning towards being lightweight. Visual Studio Code launches in a matter of seconds, and the auto-complete function is fast.
- Download Visual Studio Code for Mac. Double-click on the downloaded archive to expand the contents. Drag Visual Studio Code.app to the Applications folder, making it available in the Launchpad. Add VS Code to your Dock by right-clicking on the icon and choosing Options, Keep in Dock.
Download Visual Studio Community, Professional, and Enterprise. Try Visual Studio IDE, Code or Mac for free today.
-->This tutorial introduces the debugging tools available in Visual Studio for Mac.
Prerequisites
- This tutorial works with the console app that you create in Create a .NET console application using Visual Studio for Mac.
Visual Studio Code Macos
Use Debug build configuration
Debug and Release are Visual Studio's built-in build configurations. You use the Debug build configuration for debugging and the Release configuration for the final release distribution.
In the Debug configuration, a program compiles with full symbolic debug information and no optimization. Optimization complicates debugging, because the relationship between source code and generated instructions is more complex. The release configuration of a program has no symbolic debug information and is fully optimized.
By default, Visual Studio for Mac uses the Debug build configuration, so you don't need to change it before debugging.
Start Visual Studio for Mac.
Open the project that you created in Create a .NET console application using Visual Studio for Mac.
The current build configuration is shown on the toolbar. The following toolbar image shows that Visual Studio is configured to compile the Debug version of the app:

Set a breakpoint
A breakpoint temporarily interrupts the execution of the application before the line with the breakpoint is executed.
Set a breakpoint on the line that displays the name, date, and time. To do that, place the cursor in the line of code and press ⌘ (command+). Another way to set a breakpoint is by selecting Run > Toggle Breakpoint from the menu.
Visual Studio indicates the line on which the breakpoint is set by highlighting it and displaying a red dot in the left margin.
Press ⌘↵ (command+enter) to start the program in debugging mode. Another way to start debugging is by choosing Run > Start Debugging from the menu.
Enter a string in the terminal window when the program prompts for a name, and then press enter.
Program execution stops when it reaches the breakpoint, before the
Console.WriteLinemethod executes.
Use the Immediate window
The Immediate window lets you interact with the application you're debugging. You can interactively change the value of variables to see how it affects your program.
If the Immediate window is not visible, display it by choosing View > Debug Pads > Immediate.
Enter
name = 'Gracie'in the Immediate window and press enter.Enter
date = date.AddDays(1)in the Immediate window and press enter.The Immediate window displays the new value of the string variable and the properties of the DateTime value.
The Locals window displays the values of variables that are defined in the currently executing method. The values of the variables that you just changed are updated in the Locals window.
Press ⌘↵ (command+enter) to continue debugging.
The values displayed in the terminal correspond to the changes you made in the Immediate window.
If you don't see the Terminal, select Terminal - HelloWorld in the bottom navigation bar.
Press any key to exit the program.
Close the terminal window.
Set a conditional breakpoint
The program displays a string that the user enters. What happens if the user doesn't enter anything? You can test this with a useful debugging feature called a conditional breakpoint.
ctrl-click on the red dot that represents the breakpoint. In the context menu, select Edit Breakpoint.
In the Edit Breakpoint dialog, enter the following code in the field that follows And the following condition is true, and select Apply.
Each time the breakpoint is hit, the debugger calls the
String.IsNullOrEmpty(name)method, and it breaks on this line only if the method call returnstrue.Instead of a conditional expression, you can specify a hit count, which interrupts program execution before a statement is executed a specified number of times.
Press ⌘↵ (command+enter) to start debugging.
In the terminal window, press enter when prompted to enter your name.
Because the condition you specified (
nameis eithernullor String.Empty) has been satisfied, program execution stops when it reaches the breakpoint.Select the Locals window, which shows the values of variables that are local to the currently executing method. In this case,
Mainis the currently executing method. Observe that the value of thenamevariable is', that is, String.Empty.You can also see that the value is an empty string by entering the
namevariable name in the Immediate window and pressing enter.Press ⌘↵ (command+enter) to continue debugging.
In the terminal window, press any key to exit the program.
Close the terminal window.
Clear the breakpoint by clicking on the red dot in the left margin of the code window. Another way to clear a breakpoint is by choosing Run > Toggle Breakpoint while the line of code is selected.
Step through a program
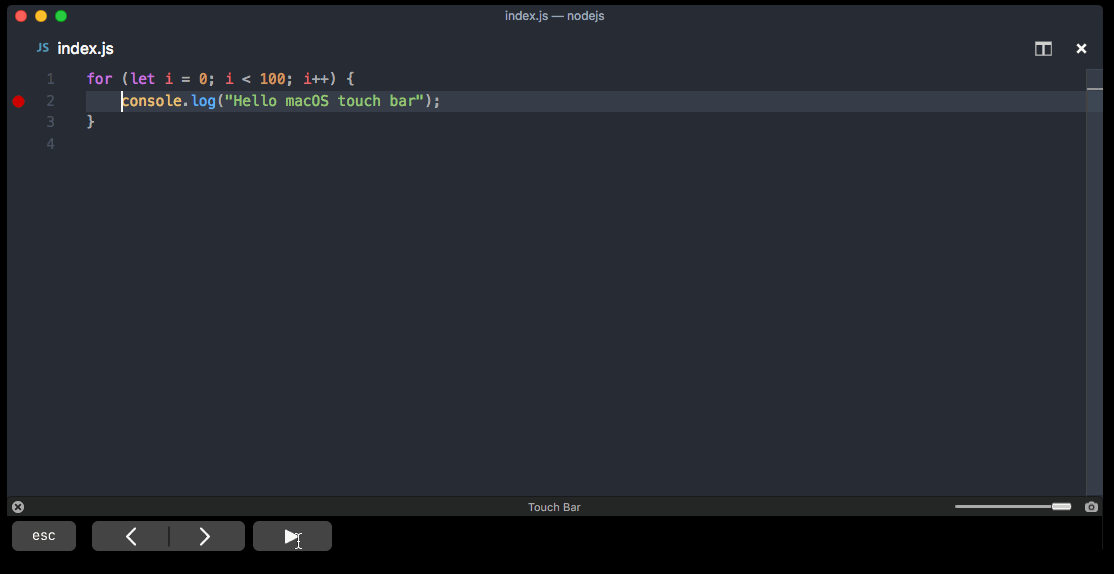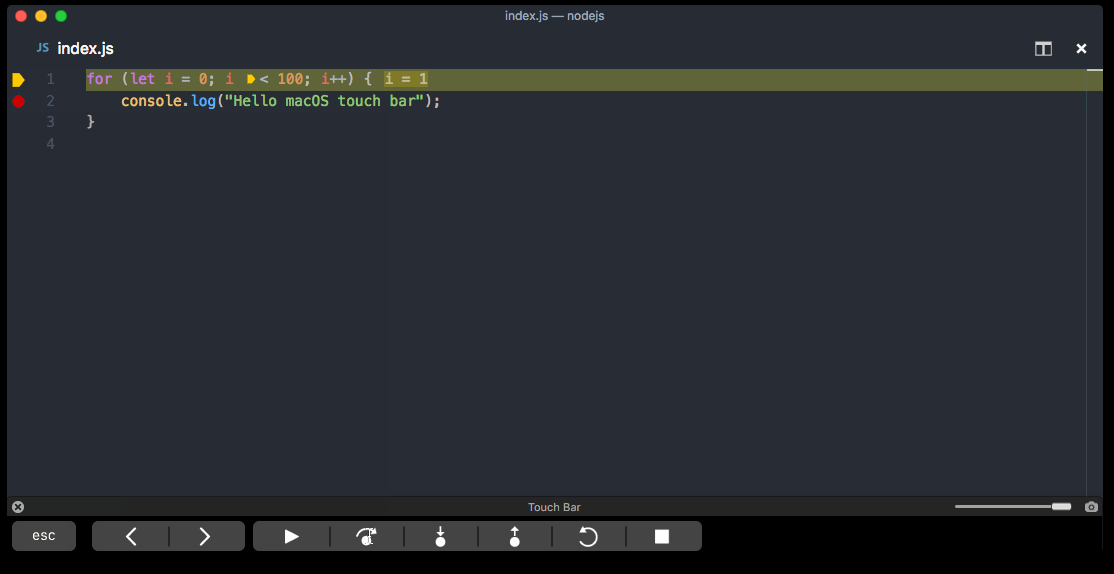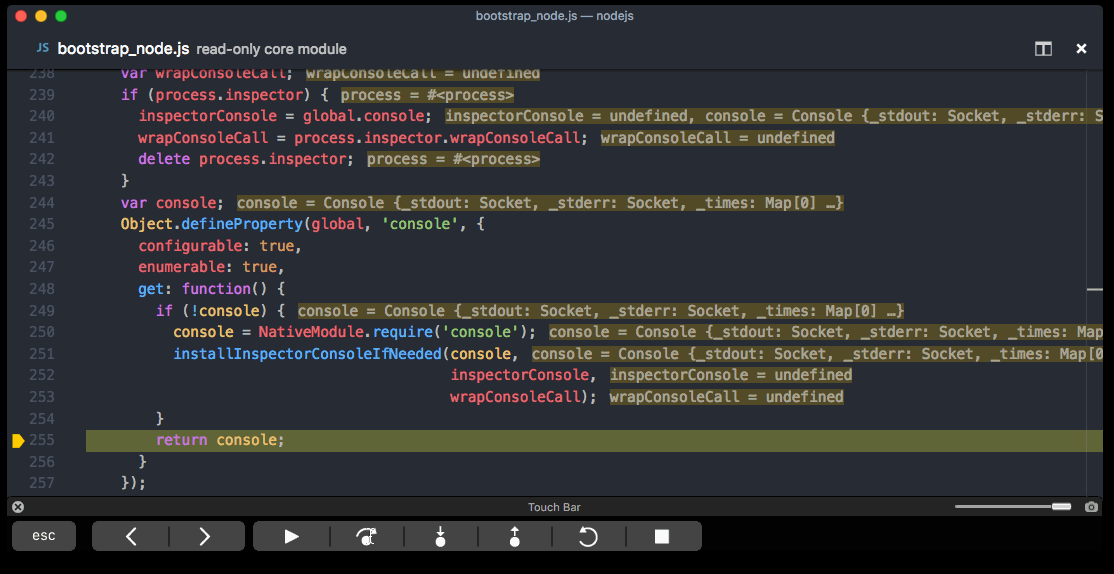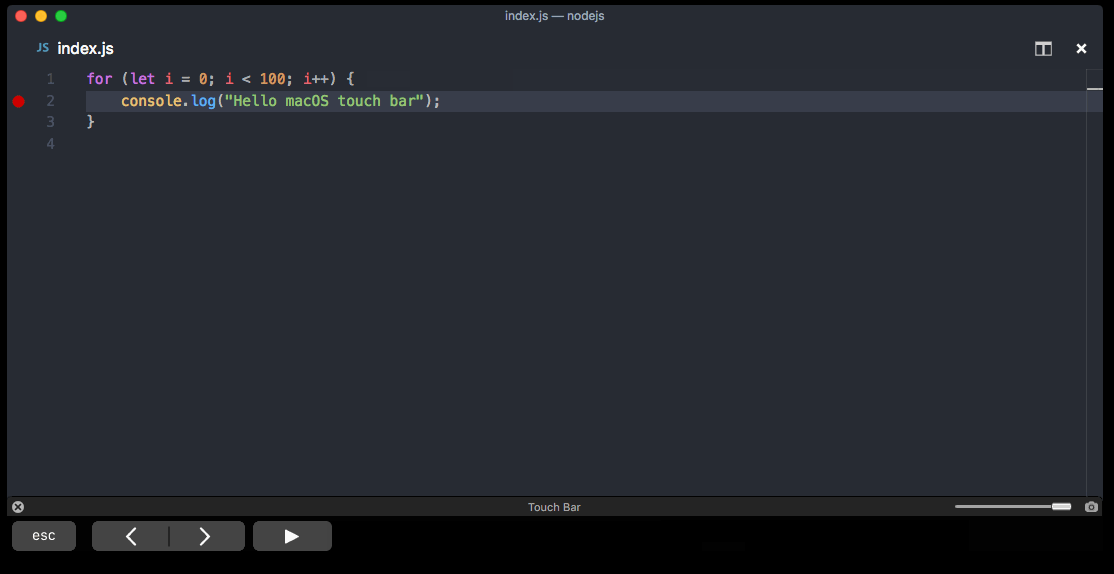
Visual Studio also allows you to step line by line through a program and monitor its execution. Ordinarily, you'd set a breakpoint and follow program flow through a small part of your program code. Since this program is small, you can step through the entire program.
Set a breakpoint on the curly brace that marks the start of the
Mainmethod (press command+).Press ⌘↵ (command+enter) to start debugging.
Visual Studio stops on the line with the breakpoint.
Press ⇧⌘I (shift+command+I) or select Run > Step Into to advance one line.
Visual Studio highlights and displays an arrow beside the next line of execution.
At this point, the Locals window shows that the
argsarray is empty, andnameanddatehave default values. In addition, Visual Studio has opened a blank terminal.Press ⇧⌘I (shift+command+I).
Visual Studio highlights the statement that includes the
namevariable assignment. The Locals window shows thatnameisnull, and the terminal displays the string 'What is your name?'.Respond to the prompt by entering a string in the console window and pressing enter.
Press ⇧⌘I (shift+command+I).
Visual Studio highlights the statement that includes the
datevariable assignment. The Locals window shows the value returned by the call to the Console.ReadLine method. The terminal displays the string you entered at the prompt.Press ⇧⌘I (shift+command+I).
The Locals window shows the value of the
datevariable after the assignment from the DateTime.Now property. The terminal is unchanged.Press ⇧⌘I (shift+command+I).
Visual Studio calls the Console.WriteLine(String, Object, Object) method. The terminal displays the formatted string.
Press ⇧⌘U (shift+command+U) or select Run > Step Out.
The terminal displays a message and waits for you to press a key.
Press any key to exit the program.
Use Release build configuration
What Is Visual Studio Code
Once you've tested the Debug version of your application, you should also compile and test the Release version. The Release version incorporates compiler optimizations that can negatively affect the behavior of an application. For example, compiler optimizations that are designed to improve performance can create race conditions in multithreaded applications.

To build and test the Release version of the console application, do the following steps:
Change the build configuration on the toolbar from Debug to Release.
Press ⌥⌘↵ (option+command+enter) to run without debugging.
Visual Studio Code Mac
Next steps
Visual Studio Code Mac
In this tutorial, you used Visual Studio debugging tools. In the next tutorial, you publish a deployable version of the app.
